Enterprise Risk Management
At Access Engineering key risks are being effectively managed through the implementation of a robust risk management framework that operates in a positive, open and honest culture.
Risk Management Framework and Process
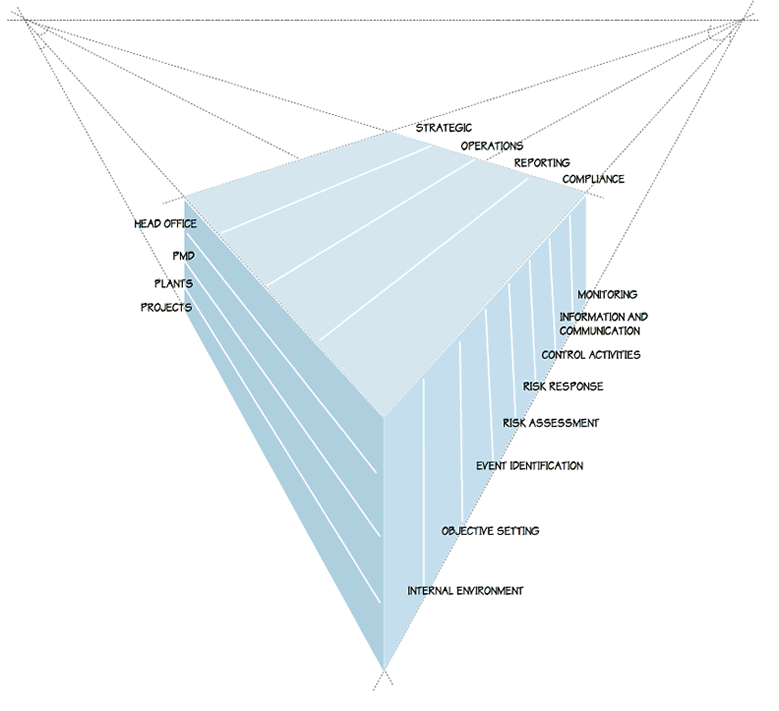
1. Internal Environment
- Strategic decisions on risk management structure and policy from Board of Directors, Audit Committee, Corporate Management and Special Committees.
- Operational decisions on risk management processes.
- Determine reporting and compliance level.
2. Objective Setting
- Identify the objectives of each project of Access Engineering PLC and the Company as a whole.
- Identify the objectives of shareholders.
- Position the audit to evaluate current status of risk management process.
- Objective setting for risk management based on Company and shareholder objectives.
- Ensure that the risk management objectives are correlated to the Company’s Vision and Mission.
- Determine the risk appetite of the organization.
Risk Appetite
Risk appetite is the correlation between risk and return of the organization. (Attitude towards risk)
3. Identify Risks (Event Identification)
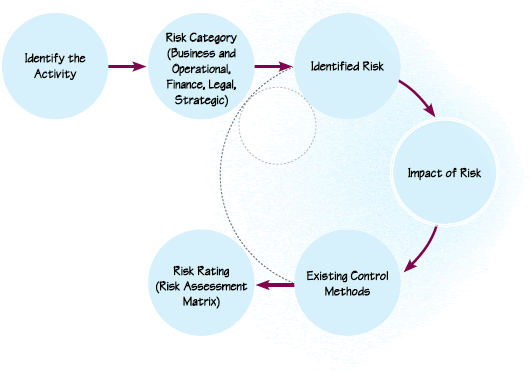
We identify the risks faced by the organization with possible categorization. The following categories are considered:
- Business and operational risks
- Financial risks
- Legal and regulatory risks
- Strategic risks
The following techniques can be used to identify risks:
- Interviews
- Trend analysis
- Research
- Predictions
- Past performances
4. Risk Assessment
4.1 Analyze Risks
Risk analysis is carried out by identifying a specific risk based on a significant activity of the Company. Risks identified in a risk portfolio which is mentioned below is then assessed based on likelihood of the occurrence and severity of the risk.
Risks are further analyzed by preparing Qualitative Risks Analysis and Quantitative Risk Analysis.
Qualitative Risk Analysis - Risk is analyzed based on the subjective evaluation of probability and impact. This method is quick and convenient due to pre-defined rating scale and flexibility. No sophisticated system would be required when carrying out this method.
Quantitative Risk Analysis - Risk is analyzed based on the probable estimate of time and cost. This method is time consuming due to the requirement of specific and large volumes of accurate information.
4.2 Evaluate Risks
This step includes risk prioritization and comparing the necessary course of action to be taken against existing internal controls.
In this process the feasibility of a course of action for prioritized risks is also evaluated in order to ensure effective allocation of resources for risk treatment.
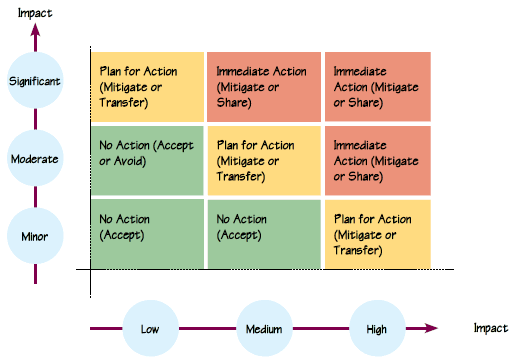
4.3 Risk Matrix for Risk Assessment
The following risk matrix is developed as a technique for analyzing and evaluating risk. This matrix mainly focuses on risk analysis based on qualitative perception.
The likelihood of occurrence of a risk is determined based on past experience, industry and organizational trends and judgment basis.
The severity of a risk is the potential financial or a non-financial loss/damage to the organization. This can also be determined based on experience, discussion, calculation, judgment etc.
Based on likelihood and severity, risks are categorized into three categories where relevant actions are proposed. Accordingly, risks need to be monitored, communicated or controlled . These three areas are identified based on the risk tolerance (appetite) limits agreed.
Assessing Likelihood of a Risk
| Value | Estimation | Descriptor | Indicator |
| 1 | Predictable. Very low likelihood. May have occurred in the past, Might be detected once or twice | Low |  |
| 2 | Occurred in the past. Anticipate significant number of incidents in working life | Medium |  |
| 3 | Occurs frequently. Anticipate higher number of incidents in working life | High |  |
Assessing Severity of Risk Based on Consequence
| Value | Estimation | Descriptor | Indicator |
| 1 | Very little evidence for loss of business based on existing consequences. Or no impact is expected | Minor |  |
| 2 | Significant evidence for loss of business due to existing impact | Moderate |  |
| 3 | Loss of business due to higher impact | Significant |  |
Plan of Action
| Value | Estimation | Descriptor | Indicator | |
| 1 - 2 | Accept the risk with no action or accept with monitoring risk while maintaining existing controls (Accept or Avoid) | No action |  |
|
| 3 - 4 | Take action to amend the existing control processes as they are insufficient before incurring severe damage. (Mitigate or Transfer) | Plan for action |  |
|
| 6 - 9 | Immediate and extensive action required due to inadequacy or ineffectiveness of current controls, with strict monitoring and controlling process (Mitigate or Share) | Immediate action |
 |
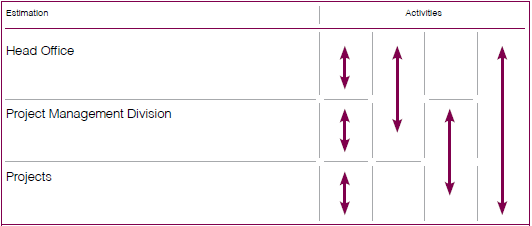
Summary of the Risk Analysis Process
Activities (Processes) of Access Engineering PLC
Risk Rating Process
5. Risk Response
Broad risk treatment approaches are identified through the risk matrix. General control approaches that can be used as Risk Treatment are -
Risk Avoidance - Avoid the risk due to unacceptability of identified risk. Not highly recommended due to correlation of risk and opportunity.
Acceptance - Risk is accepted due to insignificance, non-feasibility or ineffectiveness of an action plan. The level of risk is managed and monitored continuously.
Sharing or Transfer - One of the mitigation procedures where the risk is transferred to a third party.
Mitigation - Implementing feasible and effective strategic action plan to reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
6. Control Activities
Appropriate control methods have been taken based on the risk appetite of the Company.
7. Communicate and Consult
Effective communication is required in all stages of the Risk Management Process. Specific approaches for risk reporting need to be implemented, such as -
Risk register
Residual risk report
Identify new types of Risks
Sequent position audit
Periodic reviews
Feedback reports
8. Monitor and Review
The risk management structure/policy and framework is reviewed and updated regularly. The effectiveness of the process and actions taken is also reviewed to incorporate necessary changes.
Risk Identification
The list of risks faced by the organization on a regular basis, the consequences of the risk and current mitigation actions are mentioned in the following table. This is reviewed based on management feedback and sometimes new response action are decided based on the quantum of certain risks:
| Business and Operational Risks | Consequences | Responses |
| Project delays and cost over-runs | Could lead to penalties and negative image
This could also negatively affect securing of future projects |
Detailed project planning
Project progress review meetings Customer relationship management |
| Quality | Faulty constructions or below standard output could lead to negative image, penalties and hazards to third parties. Also earnings could be negatively affected from possible reworks | Detailed project planning
Adherence to quality and safety standards Regular internal audits |
| Product portfolio (Less diversity in income streams) | This can lead to high income volatility | Venturing to areas identified as related and unrelated diversification |
| Dependence on clients | Dependence on a few clients could lead to them dictating terms and high income volatility | Customer relationship managers to communicate regularly with the client
Approaching both private and public sector clients |
| Dependence on partners/subcontractors | Quality issues could arise and dependence could lead to unfavourable terms in contracting | Screening and review of subcontractors periodically
Working with a reliable and diverse range of subcontractors Looking for new markets |
| Staffing issues | Project execution issues | Manpower planning |
| Health and safety of employees | Could lead to workplace accidents, penalties, negative image and hiring difficulties in future projects | OHSAS certification
Providing necessary safety equipment to all sites Focused training on H&S to all employees Insurance coverage to mitigate unforeseeable risks |
| Environmental damages | Construction inherently results in changes to the natural environment. Damage of this nature will be viewed negatively by stakeholders | Green engineering philosophy
Adherence to ISO 14001 R&D into new techniques in construction which cause less impact to the environment |
| Changes in technology | Obsolescence of machinery/systems etc. | R&D |
| Competition | Increased competition has the possibility of reducing market share and margins | Efforts to maintain industry positioning
Practice of value engineering philosophy ensuring value addition to clientele Increasing efficiency through R&D Dedicated Business Development Teams continuously seeking new opportunities |
| IT systems | Information security and access to accurate information when required could be threatened | IT policy
Scheduled backup system Regular maintenance of hardware |
| Procurement Risk | Low quality material
Loss of competitive advantage Frauds |
Conduct regular supplier evaluation
Confirm the quality of material Appropriate segmentation and proper responsibility allocation |
| Human Resource Risk | Higher labour turnover
Increase in wastage |
Conduct regular evaluation and reward best performance
Conduct time based training and development |
| Plant Breakdowns | Delay in sales
Possible penalty Idling cost |
Conduct regular quality checks
Preventive maintenance |
| Wastage | Excess cash outflow | Ensure appropriate storage methods
Deliver proper instructions on material storage |
| Asset Utilization | Negative net present value
Loss of assets Compensations due to unsuitable disposal methods Cost increases |
Conduct a feasibility study prior to investment
Maintain proper documentation on asset purchase, usage, depreciation, transfers and disposals. Evaluate appropriate disposal methods prior to disposal |
| Vehicle machinery and equipment breakdown | Issues in project completion
Loss of productivity |
Conduct regular quality checks
Evaluate supplier selection criteria |
| Financial Risks | Consequences | Responses |
| Forex risk | Impact on imports and potential for asset/liability translation risk | Hedging (Forward contracts)
Matching sales and purchases to same currency |
| Interest rate risk | Potential high interest cost lowering net earnings and difficulty of financing new projects | Maintaining low gearing
Capital structure guidelines designed for each project at the planning stage Negotiations Use of various financial instruments to manage exposure |
| Investment risk | New investments could have lower yields than expected. Also certain synergies planned will be difficult to execute due to issues of value alignment | Board Committee for investment decisions Strategic Planning Committee
Investment screening and adherence to predetermined criteria |
| Liquidity risk | Inability to honor short term liabilities and incurring of unnecessary finance cost
Lenders/creditors losing trust on the Company |
Cash flow forecasting and maintaining adequate cash and cash equivalent balance
Agreed debtor/creditor settlement periods Closely monitoring project-wise net operating cash flow Maintaining cordial relationships with suppliers Secured and committed facilities from financial institutions |
| Credit risk | Potential defaults and delay of payments and their negative impact on earnings | Credit policy/approvals and regular reviews
Creditworthy client base (mainly Government) Material payments being backed by Guarantees Entering to contractual agreements with clients |
| Fraud and Error | Negative impact on earnings, image and a bad precedent for other employees | Authority limits and internal controls
Focused recruitment process |
| Inflation | Lowering of margins | Agreeing on escalation provisions as required when contracting |
| Legal and Regulatory Risks | Consequences | Responses |
| Changes in Government policy | The industry is highly prone to these type of risks and adverse changes can lead to difficulties in project planning and execution | Monitoring of policy trends |
| Tax rates | Changes in tax rates might lead to possible reduction in earnings/margins | Forecasting and tax planning |
| Compliance | Non-compliance with applicable laws and contracts could lead to fines and a negative impact on the Company’s corporate image | Adherence to corporate governance practices
Careful review of agreements |
| Strategic Risks | Consequences | Responses |
| Corporate image | Loss of contracts and a negative effect on stakeholder engagement | Continuous effort in brand/image building |
| Business growth (Industry trends) |
Inability to meet stakeholder requirements | Planning
Continuous dialogue with stakeholders |
| Business relationships | Difficult to maintain industry positioning | High focus on credible business relationship management |
| Share price | Inability to achieve shareholder return targets leading to negative investor sentiment | Maintaining sound business fundamentals
Investment screening Corporate communication |
| Talent management | Loss of business and strategy execution issues | Succession planning
Focused reward management |
The significant impacts Access Engineering has on sustainability and associated challenges and opportunities are detailed below. Further explanation can be found on the HTML web version.
| Impacts | Challenges | Opportunities |
| Economic impacts | ||
| Growth in post-war infrastructure development | Securing adequate funds
Securing resources including skilled labour |
Creation of new business opportunities
Creation of employment |
| Production of construction-related material | Cost and difficulty of securing construction plants
Mass scale operations having a negative impact on the existing small scale businesses |
Develop the existing businesses as part of the supply chain to improve the reliability and quality |
| High levels of borrowing relating to infrastructure development | Securing adequate funds to service capital and interest payments
Possible devaluation of Rupee |
None identified |
| Growth of supporting industries around construction | Maintaining acceptable levels of competition
Funding and other resource requirements |
Creation of business and employment opportunities
National level initiative to provide start-up capital and know-how |
| Faulty constructions leading to damages and fines | Meeting quality standards and maintaining corporate reputation
Rework and repair Payment of damages and fines |
Strengthen quality management practices
Use of innovative techniques in construction |
| Environmental impacts | ||
| Changes to eco-systems due to construction | Protecting the environment | Research and development (R&D) focusing on innovative techniques with less impact to the environment |
| Pollution of air, water and land | Protecting the balance of natural eco systems | Use of construction techniques that are less harmful
R&D to improve products and services Recycling, re-using and reducing products & services |
| Usage of many non-renewable natural resources (sand, stones etc) | Depletion of non-renewable natural resources, sourcing material to future projects and price escalations | Invest in new technology for reducing material requirements
Using alternative materials Recycling, re-using & reducing resource consumption wherever possible |
| Felling of trees to clear land for construction | Protecting trees | Trees planting campaigns
Reforestation Raising awareness |
| Social impacts | ||
| Creation of many employment opportunities | Procuring employees of required skill on a continuous basis
Prevention of child labour |
Training and developing employees
Raising the standards of living of people |
| Relocation of communities resulting from construction activities | Project planning
Facilitating demands of pressure groups Finding suitable locations for relocation Financial compensation |
Housing and infrastructure development projects for displaced communities
Participation of pressure groups in project planning & execution |
| Health and safety of employees when engaging in risky operations | Training employees
Providing safe working environments Maintaining reputation as a preferred employer in the industry |
Investment in H&S programmes
Raising awareness among staff Investment in new equipment and machinery |
| Professional development of employees and students involved in the industry | Establishing programmes for their professional development | CSR projects for mentoring and soft skills development
CSR projects for industry specific skill development |


